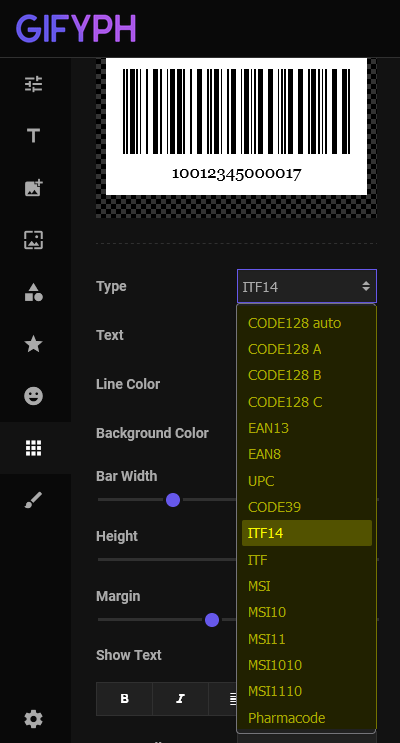
Gifyph AI Image Editor comes with Barcode generator that allows you to create fully customizable images files instantly. With Gifyph Editor You can generate most common barcode types: CODE128 auto, CODE128 A, CODE128 B, CODE128 C, EAN13, EAN8, UPC, CODE39, ITF14, ITF, MSI, MSI10, MSI11, MSI1010, MSI1110, and Pharmacode.
Barcodes are essentially a form of coded language. Each bar and space represents a specific binary digit, either a 0 or a 1. When a barcode scanner passes over the code, it reads the pattern of light and dark and translates it back into the original data. This data can then be used for a variety of purposes, such as tracking inventory, processing sales, and controlling access.
How Do I Generate a Barcode for My Product in Gifyph AI Image Editor?
Exploring the Diverse World of Barcodes
In today’s digital era, barcodes have become an integral part of business operations, from retail to logistics. Understanding the different types of barcodes is crucial for selecting the right one for your specific needs. This article delves into various barcode types, offering insights into their unique features and applications.
Understanding the Basics of Barcode Technology
Barcodes are a method of representing data in a visual, machine-readable form. Initially, barcodes were simple patterns of parallel lines, but they have evolved to include patterns of dots, concentric circles, and even hidden within images. Each type of barcode has its unique structure and usage, making them suitable for various industries and applications.
The Evolution of Barcode Technology
The evolution of barcode technology reflects the advancements in data storage and scanning technology. From the initial one-dimensional barcodes to the latest two-dimensional versions, each development has expanded the capacity and efficiency of data encoding and retrieval.
One-Dimensional (1D) Barcodes: The Traditional Choice
One-dimensional (1D) barcodes, also known as linear barcodes, are the most common type. These include the Universal Product Code (UPC) and the International Standard Book Number (ISBN), widely used in retail and publishing.
Popular 1D Barcode Types
Some of the most popular 1D barcodes include the UPC, used extensively in retail, and the ISBN for books. Other types include the Code 39, used in manufacturing and automotive industries, and the Code 128, known for its high data density and used in logistics and transportation.
Two-Dimensional (2D) Barcodes: Enhanced Data Storage
Two-dimensional (2D) barcodes, such as QR codes and Data Matrix codes, can store more data than 1D barcodes. They are used in various applications, from marketing campaigns to manufacturing and healthcare.
QR Codes: Bridging the Digital and Physical Worlds
QR codes have gained immense popularity due to their ability to be scanned by smartphones, bridging the gap between physical and digital platforms. They are used in advertising, product packaging, and even payment systems.
Choosing the Right Barcode for Your Needs
Selecting the right type of barcode depends on several factors, including the amount of data you need to store, the environment in which the barcode will be used, and the industry standards. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each type is crucial for effective implementation.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Barcode
When choosing a barcode, consider the data capacity, scanning distance, and durability against environmental factors like moisture and light. Additionally, industry-specific requirements might dictate the barcode standard to be adopted.
The Significance of Barcode Technology
Barcodes play a pivotal role in modern inventory management, data tracking, and efficient operations across various sectors. From simple retail applications to complex supply chain management, the right barcode can significantly enhance operational efficiency and data accuracy.
What Is the Most Common Barcode Type?
One of the most commonly used barcode types is UPC (Universal Product Codes). This barcode is used for labeling retail products. It’s found on almost every sale item in the market and all grocery stores in the US. It consists of a 12 digit numeric-only number. Every product is assigned its unique number by GS1, making up the first six digits of the barcode. The product’s manufacturer assigns the next five digits. Each product has a unique UPC that its manufacturers use for identification.
It helps users easily keep an eye on where their item is and when they will receive it. Other commonly used barcode types include:
- Code 39
- Code 128
- GS1-128
- Codabar
- EAN-13 and EAN-8
- ITF-14
Understanding Barcode Standards: Code 39, Code 128, GS1-128, Codabar, EAN-13, EAN-8, and ITF-14
Code 39: A Versatile Barcode Standard
Code 39, known for its versatility, is widely used in non-retail environments. It can encode alphanumeric characters, which makes it a preferred choice for inventory and industrial applications. This standard is easily readable and printable, making it ideal for diverse applications.
Why Choose Code 39?
Code 39 barcodes are suitable for small-scale applications where the amount of data to be encoded is relatively small. They are particularly useful in automotive and defense industries due to their capacity to encode a mix of numbers and letters.
Code 128: Efficiency and High Density
Code 128 is renowned for its high-density data encoding. It’s capable of encoding all 128 ASCII characters, making it a more versatile option than Code 39. Code 128 is widely used in logistics and transportation for its ability to store extensive data in a small space.
Applications of Code 128
This barcode standard is particularly useful in the shipping and packaging industries. It’s also utilized for labeling pharmaceuticals due to its high data density and compact size, which is ideal for small packages.
GS1-128: A Global Standard for Trade
GS1-128, formerly known as EAN/UCC-128, is a variation of Code 128. It’s used globally for supply chain processes, particularly in retail. GS1-128 barcodes are crucial in international trade, as they can encode data like serial numbers, expiration dates, and batch numbers.
Importance in Supply Chain
GS1-128 plays a pivotal role in logistics and supply chain management. Its ability to include additional data such as batch numbers and expiration dates makes it indispensable for tracking and quality control in the global supply chain.
Codabar: Easy Implementation for Specific Uses
Codabar is an older standard that is still in use today, primarily in libraries, blood banks, and parcel delivery services. It’s known for its simplicity and ease of printing, which makes it a good choice for organizations with limited technical resources.
Codabar’s Niche Applications
Despite being an older format, Codabar remains relevant for specific applications like library book tracking and blood bank management, where simplicity and reliability are key.
EAN-13 and EAN-8: Retail-Friendly Formats
EAN-13 and EAN-8 are primarily used in retail. EAN-13 contains 13 digits and is the standard for most products. EAN-8 is a compressed version used for smaller products. Both are essential for global retail and e-commerce.
Global Retail and EAN Standards
These formats are essential in global retail, facilitating inventory management and sales tracking. Their widespread adoption ensures compatibility and efficiency in international trade.
ITF-14: The Case of Carton Coding
ITF-14, also known as the Interleaved 2 of 5, is used specifically for marking cartons and pallets. It is a high-density barcode that can encode an even number of numeric characters and is often used to encode the Global Trade Item Number (GTIN).
ITF-14 in Bulk Shipments
ITF-14 is critical in bulk shipment processes, enabling efficient tracking and management of large quantities of products. Its design caters to the needs of wholesale and large-scale retail operations.
Choosing the Right Barcode for Your Needs
Each barcode standard has its specific uses and advantages. Understanding the differences and applications of Code 39, Code 128, GS1-128, Codabar, EAN-13, EAN-8, and ITF-14 is key to optimizing inventory management, supply chain efficiency, and retail operations. Selecting the right barcode standard is essential for meeting specific industry needs and ensuring smooth operational processes.
 gifyph.com gifyph AI Image Editor Online
gifyph.com gifyph AI Image Editor Online